A successful mobile application, sooner or later, faces the need to expand on foreign markets. While globalization rapidly affects every sphere of our lives, people still prefer using various services in their native languages. The easier, the better.
To gain marketing success in new countries, you need to take care of your users’ comfort and satisfaction, so mobile app localization is crucial. The process itself implies lots of pitfalls that you should be aware of before the start. Here is a full 10-step guide on how to localize an app for any foreign market.
What is mobile app localization?
Have you seen mobile apps that offer to choose a language on the ‘hello’ screen? You can choose the one you are comfortable with, and all application content appears in this language. Well, that is it. Localization is adapting an application’s user interface and features to fit foreign language markets. It goes far beyond simple text translation, utilizing the cultural patterns of specific countries and regions it is made for. The Android and iOs localization best practices include customizing all types of app content and elements:
Text (including buttons, alerts, notifications, etc.)
Graphics (images and video)
Audio content
Date and time format
Numbers
Currencies
Depending on the chosen locales, sometimes localization implies changing interface elements like gestures to reflect local customs. When the application is localized successfully, it looks and feels like it was initially created for a target country or region. However, it doesn’t change the original functionality and intent of the product.
Why localize your app?
People all over the world naturally tend to use mobile applications in their native language. It is much easier and quicker to master all features and get the result without a language barrier. It is usual for a startup to create an application for local use in one language version. As the application gains popularity, logically, the demand grows out of the initial location. Localization helps to reach numerous goals, including:
Entering new markets (as a result, scale business)
Gaining better visibility of the product worldwide (more App Store and Play Store users will see your app)
Increasing user engagement (more people will be able to use the app and spend more time within the app)
Boosting app downloads (better visibility leads to more downloads)
Increasing app searchability online (searching by keywords in different languages will bring new users)
Localization is essential in certain types of mobile applications that connect users from various locations. For example, if you build a dating app for an international audience, a localized UI with an integrated translator will significantly increase traffic and customer satisfaction.
Would you like to conquer new markets with your mobile application? Localize it for a native look-and-feel in the chosen locales.
Contact UsLocalization vs. Internationalization
Both terms most likely mean the same for non-developers. However, we can hardly make any comparison, as one is a must for another. Internationalization is making the application language- and culture-neutral. An internationalized app has a localization-friendly structure. Instead of hardcoding each language, it uses custom placeholders that retrieve the content in the target language to display it on the front-end.
This way, you can add languages to the website without recording it. You simply connect the files with translated content to the app codebase. The best option is performing app internationalization on the development stage, keeping in mind the need for localization in the future.
Besides text localization, such an approach helps to easily switch to various local elements like date formats and currencies. Without internationalization, it would require lots of code tweaks for every new format.
App localization in 10 steps
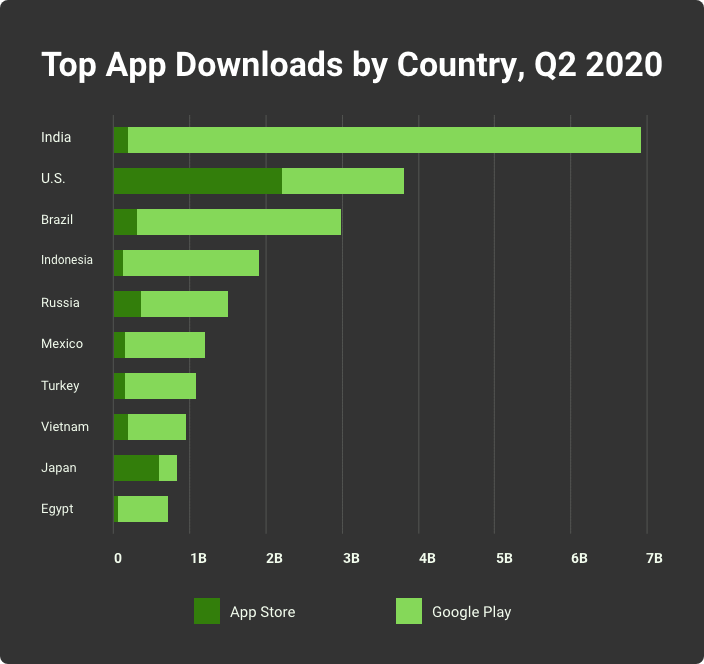
You decided to make your product friendly for non-English speaking users. That’s a reasonable move in all senses. The latest study from Nimdzi Insights, a localization research firm, revealed that 9 of 10 global users ignore the product if not in their native language. No matter what monetization model you choose for a mobile app, native-language content is much more convertible. If people can’t read it, they won’t buy it!
The main question is how to localize an iOS app smartly? To get the proper outcome, you should research, analyze, and choose the correct targets. In 2015 Airbnb's customer base grew by 700% thanks to integrating signup flow via WeChat and Weido, two top-rated web services in China. Millions of Chinese travelers became Airbnb users at once, just because the signup process was localized for them.
Research and planning here define the future outcome. Let’s start!
1. Select target locales
Most likely, you already have plans to add support for one or two languages to your mobile application. However, think wisely: it makes sense to research the market a little deeper to see where your application is potentially interesting for users. Your target is to expand your presence in the future. There are dozens of research tools and sources of information. To name a few:
Check your users’ statistics: if you see many people coming from a particular region or country, most likely, the services or goods you promote are in high demand there. It makes sense to bring a localized version of the app to that location.
Check where your competitors and category are localized: the web application with the same target audience as yours points to potentially interesting markets where you are still not present.
Google the top countries with the highest number of mobile app downloads: dozens of reports show the current figures and forecasts for growth in the coming years.
It would be easier to expand to the same locale countries (like Europe-based countries), as it requires much fewer modifications with code and data formats. Always consider potential benefits from each language added to evaluate if it is worth your efforts.
2. Define the scope of work
After you’ve selected the countries and locales for localization, define the languages for translating your application. The localization goes widely beyond simple text translations. Observe every kind of transformations you will need:
Make sure you are familiar with specific requirements for dates, currencies, and media formats for each selected locale.
Pay attention to potentially offensive gestures, emojis, and other elements that may be inappropriate for certain countries.
Define media content that should be adapted for foreign locations.
Consider integrating some popular local web services, payment systems, etc.
Make sure your app complies with local laws. If not, define the changes to do before the launch. For instance, there are limitations regarding the goods sale, and they should be unavailable in specific locations.
After you outline the scope of work, you can set the deadlines and define the team to deliver it.
3. Choose a reliable service provider
Horses for courses, as professionals say. If you want to optimize the budget and efforts for this time-consuming, scrupulous process, consider hiring a specialized team for app localization services. While you’re working on higher goals, professionals will work on its implementation.
Localization implies dozens of different work types that combine developers, translators, designers, and often marketers. You can outsource the entire complex of responsibilities or hire executors for narrow tasks, like text translation or re-arranging the app codebase. What should you take into account when choosing a localization contractor?
Check the portfolio: best app localization services providers already have success stories with other clients that can be confirmed by references.
Reliable contractors provide a free quotation after the project discussion. It will cost you nothing while demonstrating their expertise, qualifications, and interest in you as a client.
Ask technical questions: true professionals can explain any complex ideas in simple words.
Evaluate the responsiveness: it is crucial to get timely updates and stay informed during the process.
Ask for a test: you can outline your problem, then ask for a rough solution or hear about the available technical options.
Before hiring, make sure that the offered solution fits your expectations in price and timeframe. Experienced contractors always leave space for delays, potential improvements, and testing, as localization often raises unexpected challenges in the process. All these risks should be factored in a quotation.
Want your mobile application to look and feel natural for natives in any locale? Let KeyUA experts build your presence in foreign markets.
Get a Quote4. Internationalization
Before digging into the translation, you should check if your iPhone and Android apps are localizable. If the text is hard-coded, it would be impossible to make it multi-lingual. Usually, internationalization is done in parallel with app development. If not, you should do it before the localization process starts. The internationalization includes:
Code customization. The app code should not contain hard-coded texts and other elements that will be localized.
The app should be able to load content from separate files for the corresponding language or locale.
Media content like images or audio/video should change formats, lengths, and ratios depending on the locale.
The app UI needs to be adaptable for displaying texts of slightly different lengths. For instance, a button should have extra space on the sides if the translated button name will take more space than the original.
Media layering helps to save a considerable amount of time on localizing media content and prevents the app from becoming too heavy due to multiple versions of each image or video for each locale. You can put inscriptions separately from the images or put subtitles above the video.
There is no typical internationalization scheme, as the work scope highly depends on the chosen locales and their requirements to data formats, graphics, texts, numbers, dates, etc.
5. Translating texts
It may seem that you can go without professional assistance, as translating button names and menu items are easy for a Google Translator. However, even simple words have multiple meanings, and Google Translator often chooses the wrong variant for translation that misleads and confuses users. You want your application to look and feel natural in a new language so that native users will feel comfortable using it. For this purpose, you need to hire a professional translator (or a few translators). Besides far better translation quality, professionals will do the job much faster.
As a rule, texts for translation are collected to XML or XLIFF files. Each text phrase, button name, menu items, and other elements are separated into strings. For better translation, it would be useful to comment on the text strings to explain better how this or that phrase is used in the UI. It is unnecessary to comment on every expression, just the ones that can have double meaning or used in some non-standard sense. Even if you hired professional translators, do your best to assist, as no one knows a mobile application better than its creator.
A translator usually works with texts directly in these files or uploads them into the translation management system (TMS). The most popular TMS systems for localizing mobile applications are Smartling, Phrase, LingoHub, Crowdin, Localize, and Crowdin.
Using TMS is preferable for big apps with much text content and many repeated elements. There are a few essential advantages:
It helps to keep all translations in proper order.
Eliminates different translations for the same phrase (if it is present in numerous parts of the app and translated by other people).
It speeds up the process, as it identifies previously translated phrases and strings stored in a database. There is no need to translate the same words again and again.
Usually, TMS is multi-platformed, allowing both iOS and Android app localization within one tool.
You can track the progress and see how much time is spent on it.
It syncs the work of all translators, keeping the deliverables in one storage.
After the text is translated, the XML (XLIFF) file for the new language is generated and connected to the app code on the backend.
6. Localizing media
There are three approaches to consider when localizing media content:
Technical: there are certain limitations regarding image and video formats for different locations.
Cultural: images and photos should be either culture-neutral or different for each locale to reflect its culture. For instance, Asian customers may not recognize an ambassador of some European fashion brand. It would be reasonable to invite a local star to represent the brand in the Asian market.
Ethical: avoid any inappropriate elements that may be offensive for users from your supported countries.
Also, multimedia content is a potent marketing tool. By providing localized catalog photos or video tutorials, you can boost sales and user engagement in supported regions. For instance, you have a fitness application with recorded video workouts and tutorials for different exercises. Of course, the user needs to understand the instructions to subscribe and train.
If you are using gestures like ‘thumb up’ or ‘rock on’ in your UI, take care to check their meanings in the countries you’re going to support.

If you need different image versions for other locales, use the same coding approach as with texts. Don’t hard-code the links to images. Substitute it with placeholders to retrieve specific image URL depending on the chosen language.
7. Localize your app store pages
Localizing Google Play and Apple App Store helps to increase the overall exposure. Take care to create product page versions for every language your app supports. It also improves rankings in the app markets, as every new language increases the number of keywords you can rank for.
The App Store has 40 available languages and 155 countries. Google Play supports 77 localizations (country-language). Also, there is an auto-translation feature. If you haven’t localized your content on the product page, Google will translate it automatically if a reader enables the ‘translate’ option. Though the auto-translation algorithms continuously become better, it is still an issue. The text translated automatically may pervert the original meaning. Also, readers consider machine translation as a disregard.
Localize the entire product page instead of separate sections. Choose correct keywords for each language, localize screenshots, videos, and texts.
8. Testing
Testing should not be an ‘after’ stage of your localization process. It would be much better to run continuous localization testing in parallel with all code modifications and translations. The overall scope of work for localization testing includes:
Checking all modules affected by localization
Culture- and location-specific modules
Testing major business scenarios in new locations
Compatibility tests across target regions
Checking linguistic and typographical errors
Verifying the adherence to the environmental standards for the input and display
Usability testing of the UI
Checking the UI for cultural appropriateness in colors, design, images, etc.
There are numerous testing approaches for mobile application localization— functional, linguistic, and user testing are usually combined. Tests are never enough when it comes to applications. Usually, the process begins with automated and manual testing by QA specialists and ends with beta testing before the public release. Beta testers are a closed group of real users checking how the app works in natural conditions. Their feedback is an excellent source for further development. Even if no critical bugs are found, you will get some inspiration for optimization and improvements.
9. Marketing materials to support the release
After testing is over and your app is ready for launch, it’s finally time to make a release. Upload the new app version to app stores, enable newly available locales, and put all localized texts and multimedia content for the app store listings.
How will people find out about your new supported markets? You should prepare marketing materials and launch new ad campaigns on the targeted audience. Usually, the app team posts press-releases and news posts on its social network accounts (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter) and shares this news on forums and other topic resources online. Online advertising also works well for the app to become noticed in a new market location.
When combined with localized app market pages, such marketing promotion helps increase downloads in new locations, keeps your product’s interest up with existing users, and prompts them to appear in various app charts and reviews.
10. Collect feedback
When working on something for a long time (an app localization usually takes a while), you can lose focus and overlook some minor bugs. Some words may be misused, or there will be a button left without translation. Real users will notice that very quickly. After appearing on new markets, get ready to get lots of user reviews and questions regarding your app. You will need to provide some support in that language, so understand the reviews and questions and give an adequate reaction. It plays an essential role in building the app reputation and winning user notoriety.
Final thoughts
Localizing a mobile app is trickier than it seems at first glance. It can be challenging if you do not have enough marketing specialists, developers, designers, and translators in your current team. However, it should not slow down your company's growth. If your app needs to enter foreign markets confidently, seek professional assistance with customer comfort in mind. KeyUA is ready to help with all mentioned steps, from analyzing your audience for potentially interesting locales to testing and launching the localized app to new markets. We use the best technologies and software for accurate localization, timely deliverables, and comprehensive marketing analytics. Go for the experience, reliability, and technical and linguistic perfection with KeyUA.
Has your app grown up and needs to conquer new markets? Localize it wisely with KeyUA!
Book a Call




 Unit 1505 124 City Road, London, United Kingdom, EC1V 2NX
Unit 1505 124 City Road, London, United Kingdom, EC1V 2NX
Comments
Leave a comment